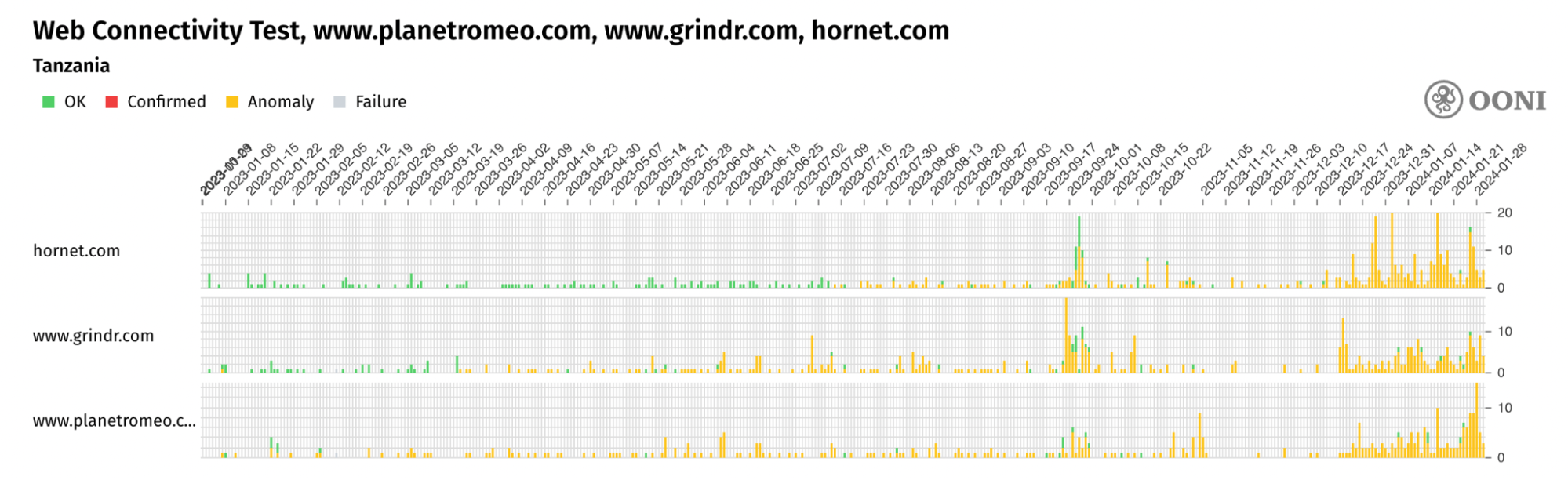
The results of our analysis show that most ISPs in Tanzania appear to implement blocks by means of TLS interference, specifically by timing out the session after the ClientHello message during the TLS handshake. As the timing of the blocks and the types of URLs blocked are (mostly) consistent across (tested) networks, ISPs in Tanzania likely implement blocks in a coordinated manner (possibly through the use of Deep Packet Inspection technology).
You must log in or # to comment.